Smart Analytics#
Smart Analytics is a transformative capability that empowers users to generate tables from existing datasets or external databases, enabling a multitude of analytics operations. This feature offers more than just table generation – it also allows for the seamless appending of table values to existing tables or the creation of new tables, facilitating streamlined data consolidation and enrichment. By Smart Analytics, users gain the flexibility to create and publish datasets while simultaneously creating, updating or overwriting tables using Smart Analytics queries. This concurrent process enhances the efficiency of data management, ensuring that the most up-to-date information is readily available for analysis and reporting purposes.
The dynamic functionality of Smart Analytics enables users to run algorithms and produce data that can be directly fed into tables, eliminating the need for manual data connections. This capability empowers users to efficiently leverage their data assets, whether it involves creating new tables or updating existing ones.
Data Connection#
Smart Analytics offers versatile ways to obtain data. Users can acquire data through different methods, such as retrieving it from existing datasets within our platform or connecting to their own database for data access.
For an example, let’s retrieve the data from our pre-existing dataset within the ConverSight platform.
Let’s initiate by importing the required library files from the ConverSight Library. It’s important to note that Smart Analytics has its own distinct library within ConverSight.
from conversight import Dataset,Context,SmartAnalytics
# This will import all the necessary libraries
NOTE
The keyboard shortcut Shift + Enter is utilized to execute a cell.
The connection to the dataset is established using the dataset ID and token. The token ID can be obtained from the Content Library, which can be accessed for user and session-related details
ctx=Context()
# ctx object is used to obtain user related session details
NOTE
The keyboard shortcut Shift + Tab is used to view the help guide for a method.
The dataset should be populated with the necessary arguments to enable access to its data.
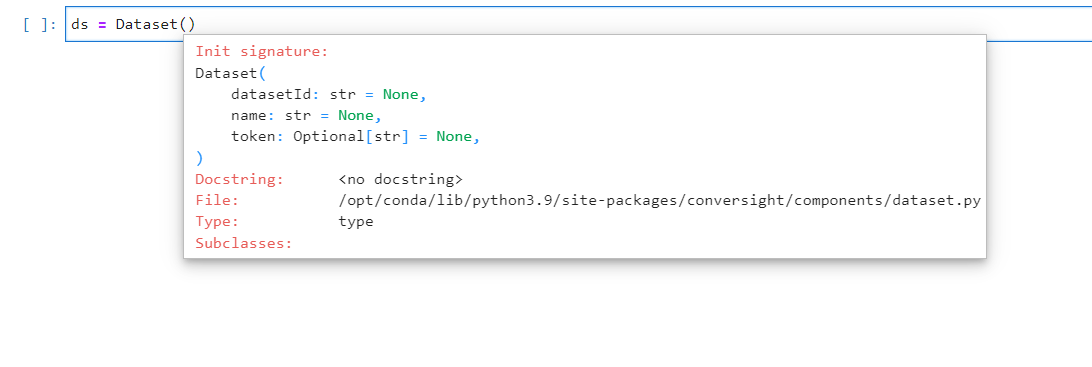
Arguments for Dataset Access#
ds = Dataset('Dataset_ID',token=ctx.session.token)
The object ‘df’ contains the dataframe obtained by executing a query in the Dataset and saving the result.
df = ds.sqlDf("SQL QUERY")

Dataframe#
Select smart analytics from the ds object.
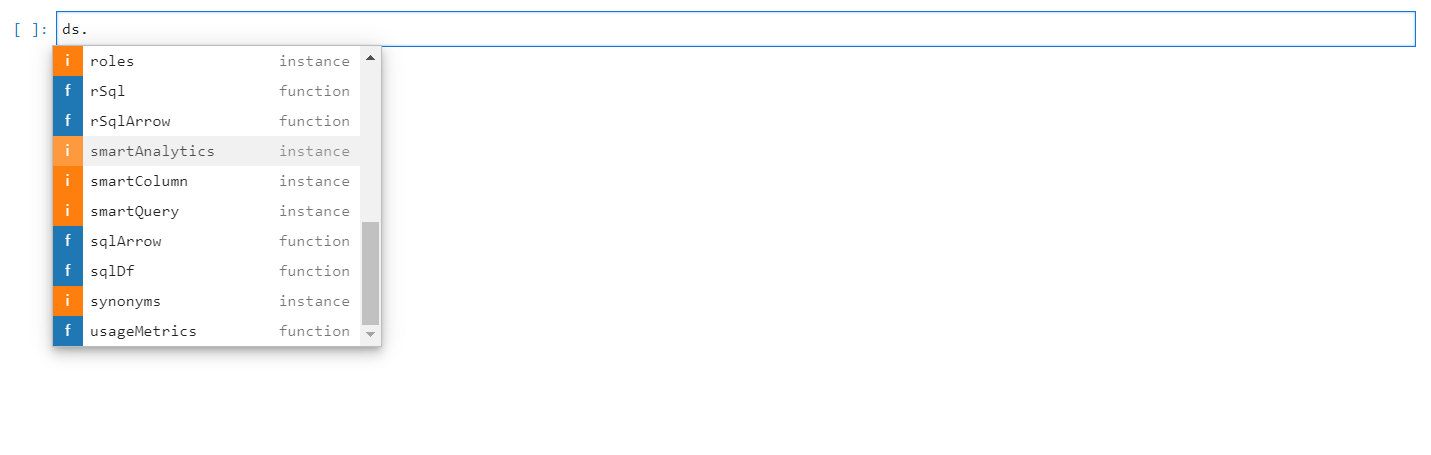
Smart Analytics#

Smart Analytics#
Available Methods in Smart Analytics#
Pressing the Tab button on an object or function displays a list of the available functions. List of available methods for Smart Analytics are shown in the below screenshot.
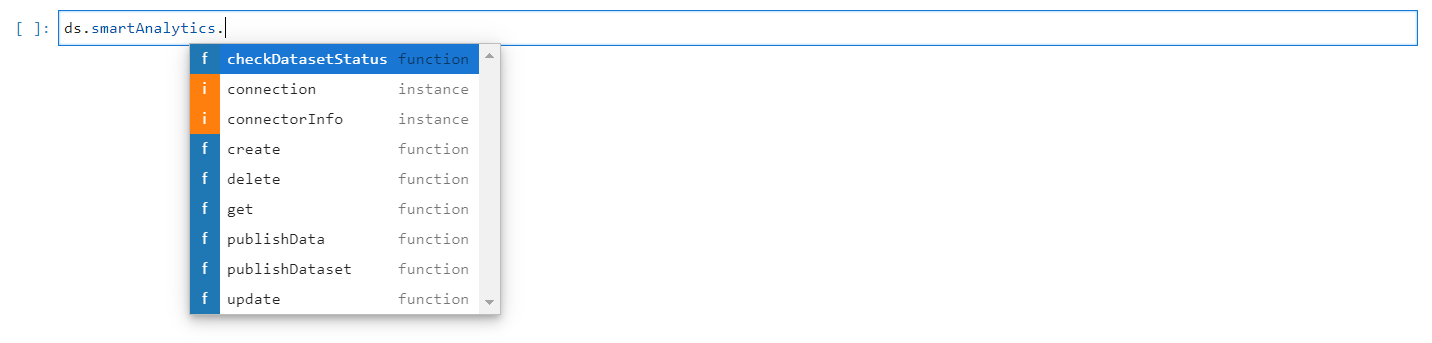
Methods in Smart Analytics#
Create#
The create method is employed to generate a new Smart Analytics. Furthermore, it can also be used to update an existing table. If the “isOverwrite” parameter is set to “True,” the method will overwrite an existing table by truncating the current data. Alternatively, if “isOverwrite” is set to “False,” the method will append the new data to the existing data. The required arguments for creating Smart Analytics are provided below.
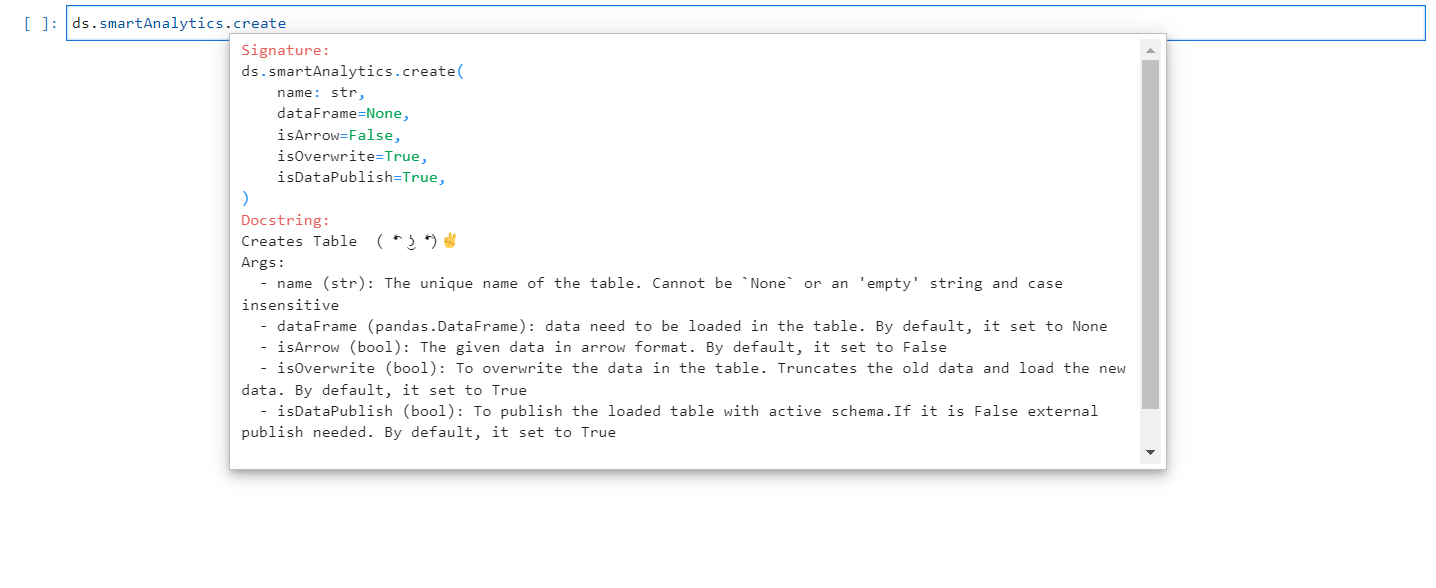
Create Method#
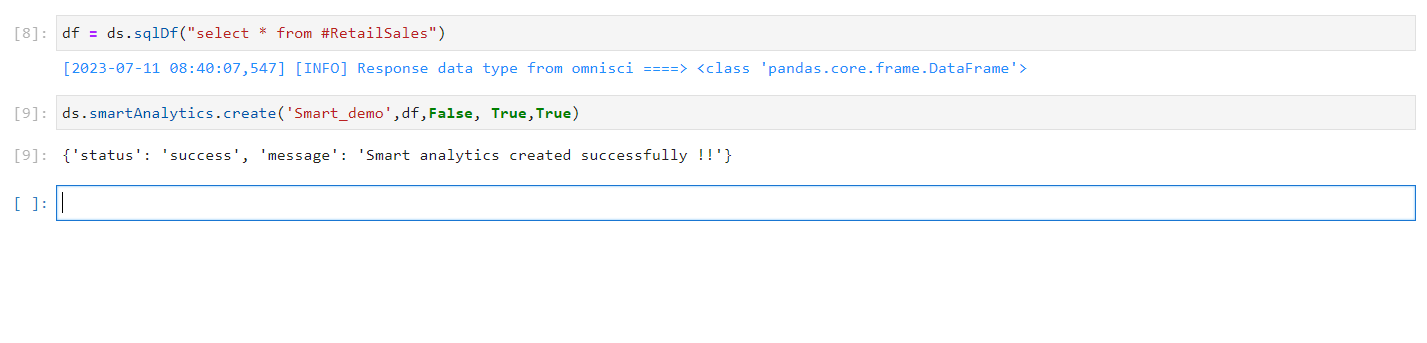
Smart Analytics Created#
Update#
The update method is used to modify an existing Smart Analytics. If the “isOverwrite” parameter is set to true, it will overwrite the existing table by truncating the current data. Otherwise, it will append the new data to the existing table. The required arguments for updating a Smart Analytics are provided below.
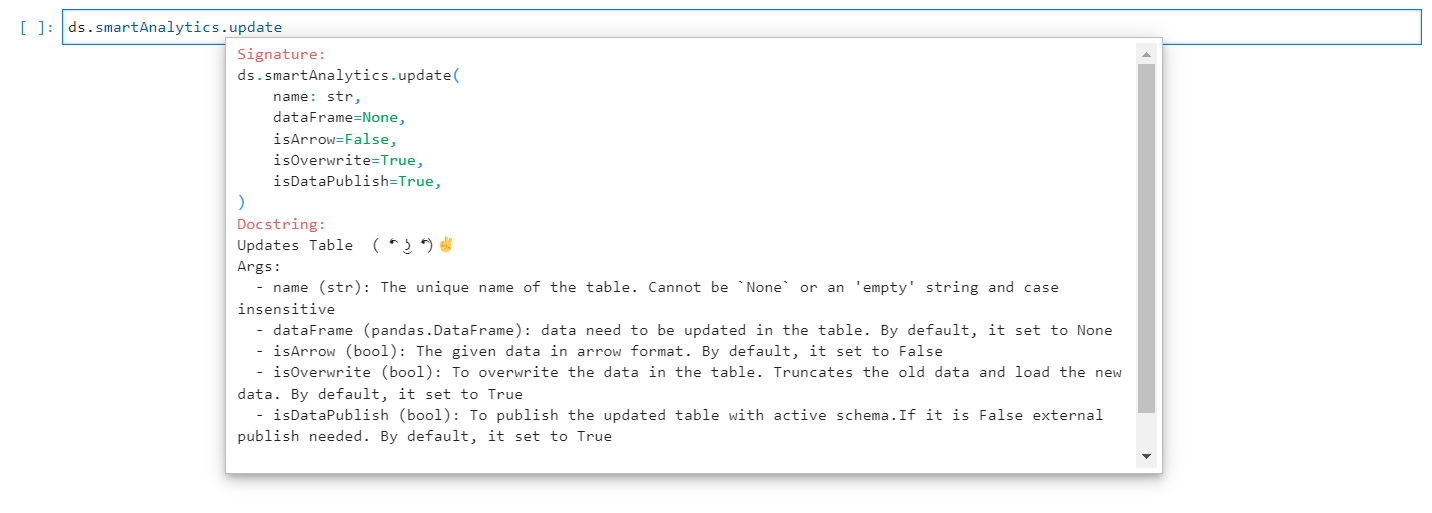
Update Method#
NOTE
When the isOverwrite parameter is set to true, it replaces the data in the table by truncating the old data and loading the new data.
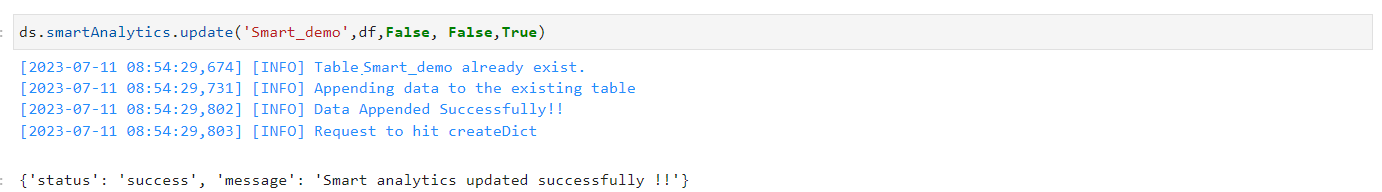
Smart Analytics Updated#
PublishData#
The publishData method allows for the publication of the SME without the need for any manual intervention. It grants the privilege to publish directly from the notebook. This method does not require any arguments.
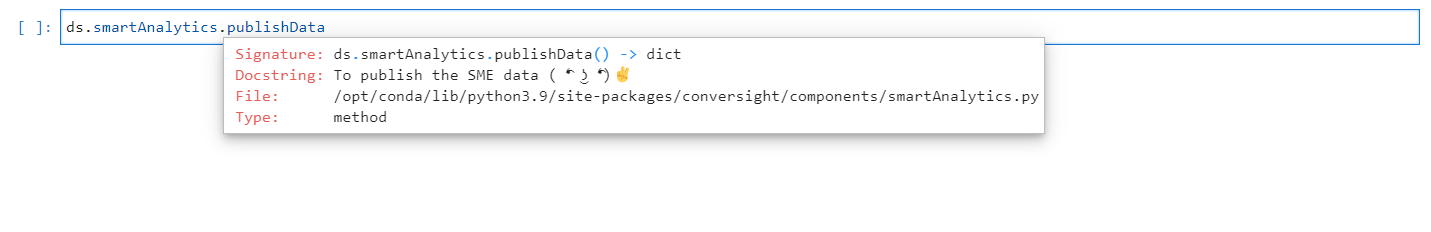
PublishData Method#
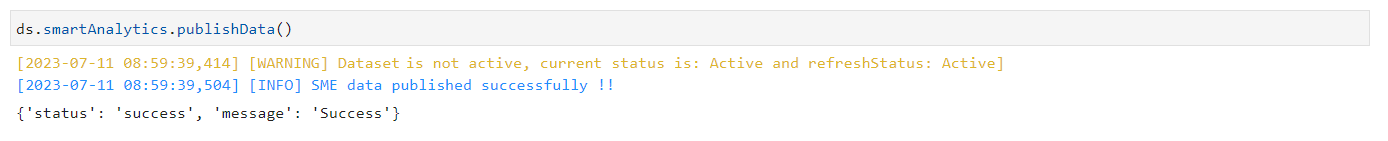
Smart Analytics Published#
Get#
The get method is utilized to list out the Smart Analytics that have been created for the connected dataset. This method does not require any arguments.
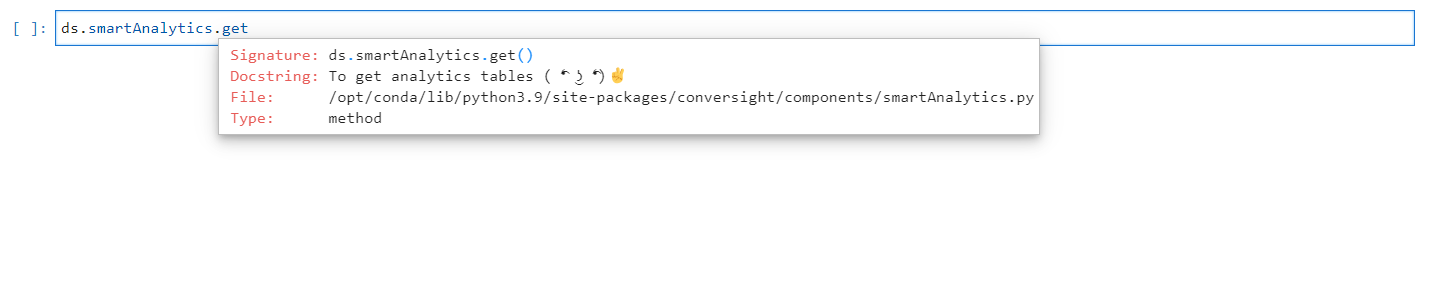
Get Method#

List Of Smart Analytics Available#
PublishDataset#
The publishDataset method is utilized to publish the Smart Analytics. The argument for the publishDataset method is used to determine the action to be taken. By default, it is set to update, which updates the dictionary for the specified tables. To publish newly created tables, use create as the argument. The object arguments are used to either publish the specified objects or update the dictionary for the given objects. When creating or updating the Smart Analytics using the create and update methods, if the “isDataPublish” argument is set to “True,” the Smart Analytics will be created or updated accordingly and the changes will be reflected in SME Coaching (Subject Matter Expert) automatically. However, if “isDataPublish” is set to “False,” the created or updated Smart Analytics will be saved in temporary data and will not be reflected in SME unless it is explicitly published using the publishDataset method.
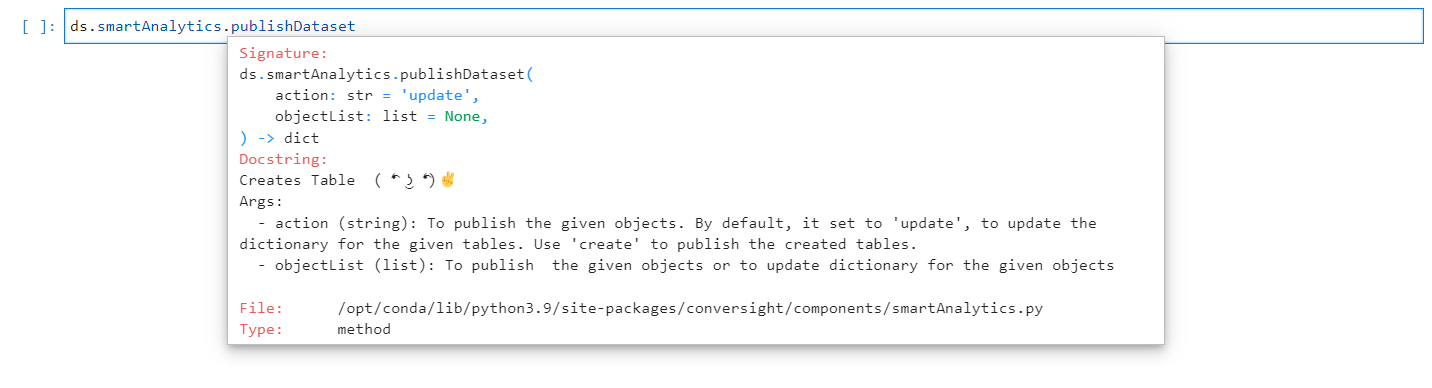
PublishDataset Method#

PublishDataset#
NOTE
The object arguments in publishDataset method can contain multiple unpublished Smart Analytics that can be published simultaneously.
Delete#
The delete method is used to delete Smart Analytics. It takes the name of Smart Analytics as an argument. The isDataPublish parameter is used to determine the type of deletion. If set to False, the raw table will be deleted. If set to True (default), the schema table will be deleted. Deleting the raw data allows for reusing the tables with the existing schema. However, deleting the schema will completely remove the table.
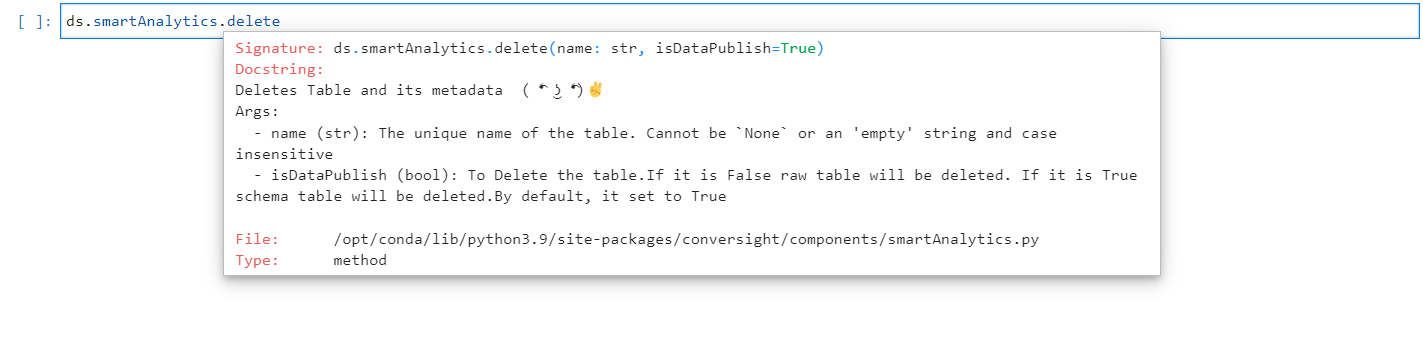
Delete Method#
Smart Analytics Deleted#
NOTE
When a Smart Analytics is created or updated with the "isDataPublish" argument set as "False," it can be deleted using the delete method by setting the "isDataPublish" argument in the delete method as "False" as well.
Smart Analytics empowers users to generate tables from existing datasets or external databases, facilitating various analytics operations. It offers seamless appending of table values, creation of new tables and concurrent dataset creation and table management. This dynamic capability eliminates the need for manual data connections and enhances data management efficiency for analysis and reporting purposes.